The majority of new homes built in the US have central air conditioning as a standard feature. And, if you live in the South, air conditioning may be essential. When choosing an air- conditioning unit, check the current regulations. The US Department of Energy requires that all central home units sold in the U.S. must achieve a seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) of 13, which also is the rating for Energy Star. The SEER rating is calculated by dividing the total amount of heat removed from the air by the total energy required by the air-conditioning unit.
Lots of information on Household Appliances here.
AIR CONDITIONERS
Whether it is a whole-house system that works alone or with a heating system, or a series of room units, the basics of how an air conditioner works is the same. Air conditioners pull warm air out of the space, filter it, cool it, and then release that cool air back into the space. The biggest energy user in any air-conditioning unit is the compressor, which pumps the refrigerant through the air-conditioning system to cool the space.

Air-conditioning unit: As long as the air conditioner
is sized properly for the space it is intended to cool, you will be able
to achieve the same type of results from whole-house and single-room
systems. The air conditioner shown here can be used with a heat pump.
Don't forget to clean your room air while "air-conditioning"!
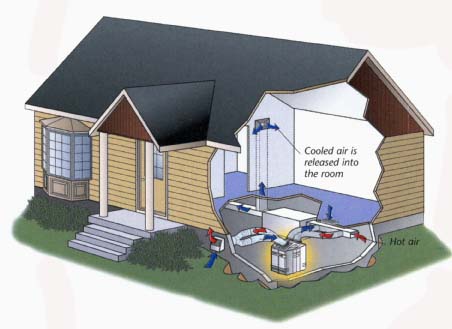
Cold air distribution: Central air conditioners can work with a furnace.
The furnace blower and the furnace’s ducting are used to deliver the
cooled air from the air-conditioning unit around your home. Shown here,
the cold air is represented by the blue arrows. The cold air leaves the
furnace in the basement, travels through the ducts until it reaches the
vents in a room.

Hot air return: Air conditioners not only supply the house
with cool air, they also pull the warm air out of the room and expel it
outside of the house. Shown here with red arrows, the warm air is sucked
from the room into the air-conditioning unit in the basement, where the
heat is extracted and expelled to the outside.
COOLING OPTIONS
Air conditioners are not the only way to keep a house cool when the temperature rises outside. Ceiling fans, attic fans, proper insulation, and shades covering the south side of the house also help circulate air and keep heat from building up inside your home.
ROOM AIR CONDITIONERS
If you want the benefits of air conditioning but are unable to install
a whole-house system, wall or window units are available to condition
a smaller space. Window units have adjustable sides and can be set inside
an open window. Wall units are installed flush into an exterior wall.
Just as with whole-house systems, you will need to regularly clean the
filter to make sure it is functioning efficiently.
More on Room Air
Conditioners from the U.S. Dept. of Energy.
Previous: Geothermal Heating | Next: Radiators and Baseboard Heaters