While the details of wood-frame building construction may vary in different localities, the fundamental principles are the same. The following figures, charts, and tables show established methods of construction and accepted practices used in wood-frame building construction.
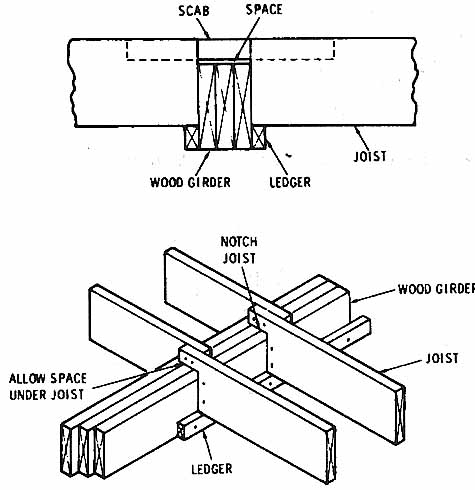
Fig. 1. (a) Connecting scab used to tie joists together. (b) Floor joists
notched to fit over girder.
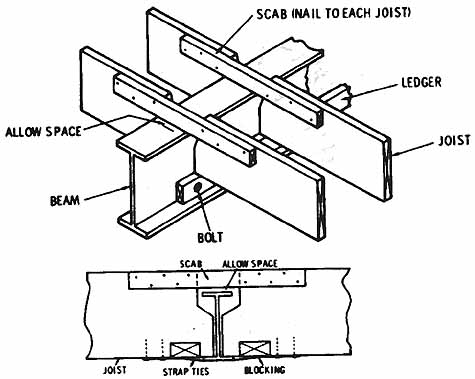
Fig. 2. (a) Floor joists resting on wooden ledger fastened to "I" beam
girder. (b) Floor joists resting directly on "I" beam girder
and connected at top with scab board.
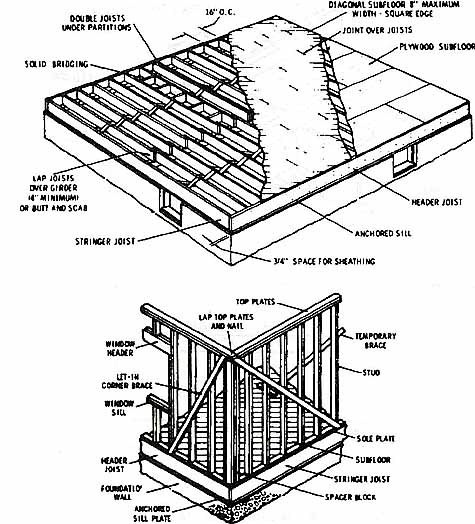
Fig. 3. (a) Platform construction--details of floor joists and sub-flooring.
(b) Platform construction--wall studs with let-in bracing and double
top plates.
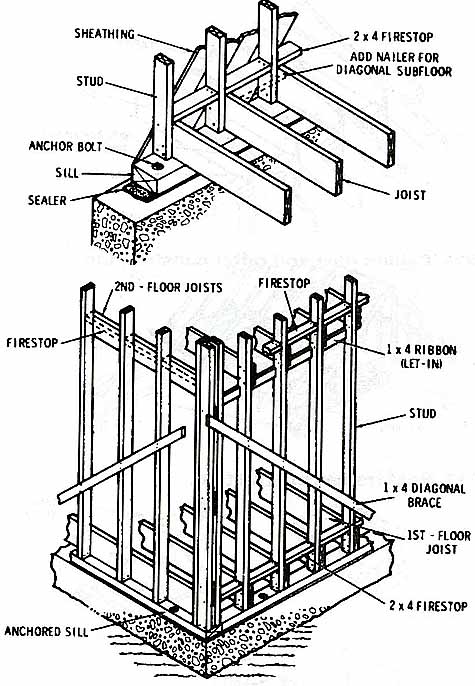
Fig. 4. (a) Balloon-frame construction-wall studs and floor joists rest
on anchored sill. (b) Balloon-frame construction-second-floor joists
rest on 1" x 4" ribbons that have been let into the wall
studs. Fire stops prevent spread of fire through open wall passages.
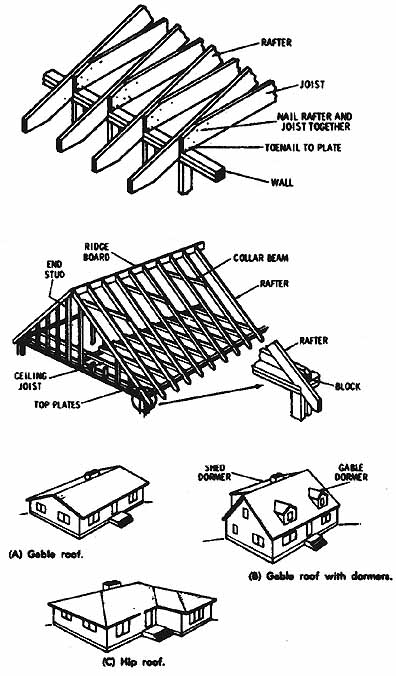
Fig. 5. (a) Ceiling joist and rafter construction. (b) Roof frame construction.
(c) Frame roof styles.
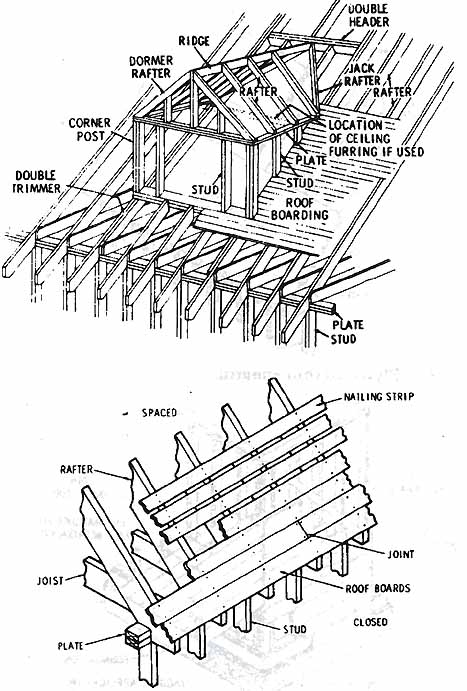
Fig. 6: (a) Dormer-frame construction. (b) Board roof sheathing-spaced
for wood shingles or closed for asphalt shingles.
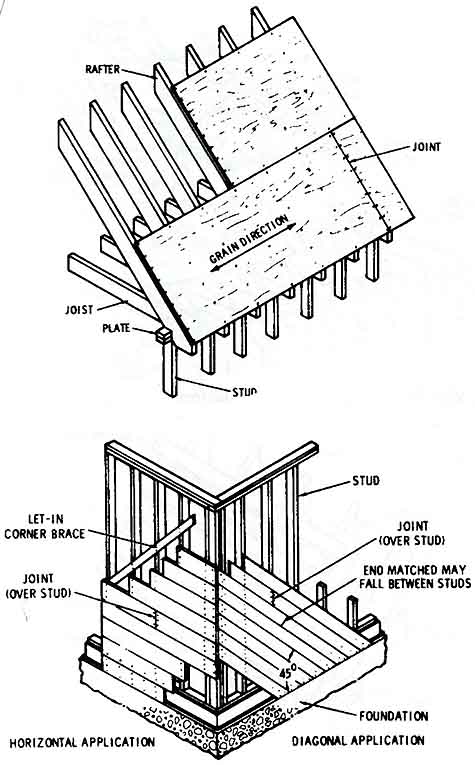
Fig. 7. (a) Plywood roof sheathing. (b) Horizontal or diagonal applied
board wall sheathing.
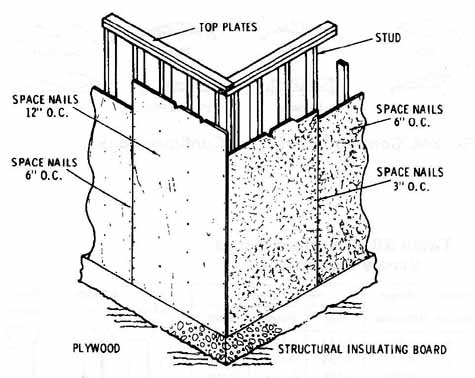
Fig. 8. Plywood or insulating board wall sheathing.
Home • •